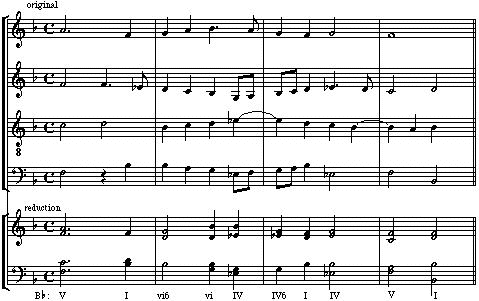Polyphonic Texture Example

The following excerpt represents monophonic texture 07 true.
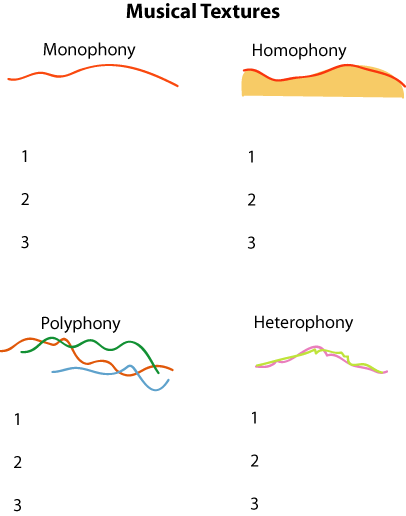
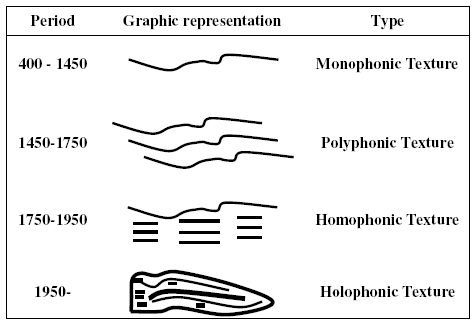
Polyphonic texture example. If polyphonic determine whether the texture is. Polyphonic music can also be called polyphony counterpoint or contrapuntal music. Within the context of the western musical tradition the term polyphony is usually used to refer to music of the late middle ages and renaissance. If more than one independent melody is occurring at the same time the music is polyphonic.
See counterpoint examples of polyphony rounds canons and fugues are all polyphonic. This music passage is an example of. Polyphony means different sounds or voices. Homophony is the texture we hear most in pop music on the radio film music jazz rock and most classical music of the last century.
Polyphony is a type of musical texture consisting of two or more simultaneous lines of independent melody as opposed to a musical texture with just one voice monophony or a texture with one dominant melodic voice accompanied by chords homophony. Polyphonic music has parts that weave in and out of each other. Polyphonic imitative one or more parts imitates echoes the melody present in one of the other parts polyphonic nonimitative two or parts that are relatively equal in importance but do not include parts that imitate one another. This music excerpt is an example of.
Polyphonic music is a musical texture that describes a style of composing with multiple simultaneous melodies. The following excerpt represents polyphonic texture. Homophonic texture also called homophony is by far the most common type of texture found in music today the other two main types of texture are monophonic and polyphonic. A mixture of polyphonic and homophonic textures.
The following excerpt represents monophonic.